Try a quiz
Select one of the options below to try a quiz of this level. Upon selecting an option, the corresponding categories to the different levels will be identified. Please note these categories can be modified in the section "Create your own quiz".
Create your own quiz
Select a question type:
Select structures with:
Select a category of compounds (More info)
|
A hydrocarbon connected by only single bonds. |
 |
|
A hydrocarbon containing at least one double bond, which does not have any stereoisomers. |
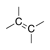 |
|
A hydrocarbon containing at least one double bond, which has one or more stereoisomers. |
 |
|
A hydrocarbon, in which the carbon chain forms a cycle. |
 |
|
A hydrocarbon that forms a ring of any size. |
 |
|
A hydroxyl group bound to an sp3-hybridized carbon. |
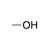 |
|
An oxygen atom between two sp3-hybridized carbons. |
 |
|
A three atom ring containing one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms in which all atoms are sp3-hybridized. |
 |
|
A carbonyl group in which the carbon is bound to a hydrogen as well as another carbon. |
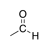 |
|
A carbonyl group in which the carbon is bound to two other carbons. |
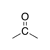 |
|
Two alkoxy groups (OR, R=alkyl) bound to an sp3-hybridized carbon. |
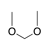 |
|
A carbonyl group in which the carbon is bound to an alkoxy group (OR, R=alkyl) and another carbon. |
 |
|
A carbonyl group in which the carbon is bound to a hydroxyl group (OH) and another carbon. |
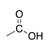 |
|
A neutral, sp3-hybridized nitrogen atom, bound to sp3-hybridized carbons and/or hydrogen atoms. |
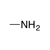 |
|
A carbon-nitrogen triple bond. |
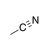 |
|
A three atom ring containing one atom of nitrogen and two of carbon in which all atoms are sp3-hybridized. |
 |
|
A nitrogen atom bound to two oxygen atoms, in which one bond is single and the other is double. |
 |
|
A carbon-nitrogen double bond in which the carbon atom is bound to two other carbon atoms. |
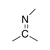 |
|
A carbonyl group in which the carbon atom is bound to an amino group. |
 |
|
A thiol group (SH) bound to a sp3-hybridized carbon. |
 |
|
An sulfur atom between two sp3-hybridized carbons. |
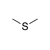 |
|
A carbonyl group in which the carbon atom is bound to a sulfide group and another carbon atom. |
 |
|
A halogen atom bound to a carbon atom in an alkyl group (X = F, Cl, Br, I). |
 |
|
One to six substituents on benzene ring. (An example is presented on the right). |
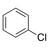 |
|
A ring containing at least one atom other than carbon, which does not satisfy the rules of aromaticity or antiaromaticity. (An example is presented on the right). |
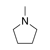 |
|
A ring containing at least one atom other than carbon, which satisfies the rules of aromaticity. (An example is presented on the right). |
 |
|
A class of hydrocarbons in which the molecules are composed of isoprene units (2-methylbut-1,3-diene). (An example is presented on the right). |
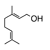 |
|
A halogen bound to the carbon of a carbonyl group (X = F, Cl, Br, I). |
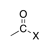 |
/




